Vulnerability and Penetration Testing – Key Aspects of Cyber Security and Necessary Parts of NIS2 Compliance
What Are Vulnerabilities?
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses, bugs or flaws in software, hardware or network infrastructure that can be exploited for unauthorised access, data leaks or other attacks. These vulnerabilities can exist in operating systems, web applications, databases, network devices and other technologies.
Why Are Vulnerabilities Dangerous?
- Attacks on vulnerabilities can lead to leaks of sensitive information, financial losses or service disruptions.
- Malware and exploitation: Vulnerabilities are often targeted by malware and attackers who exploit them to infect systems or gain unauthorised access.
- Loss of trust: Successful attacks on vulnerabilities can damage an organisation’s reputation and reduce customer trust.
Penetration Testing – What Is It And How Does It Help?
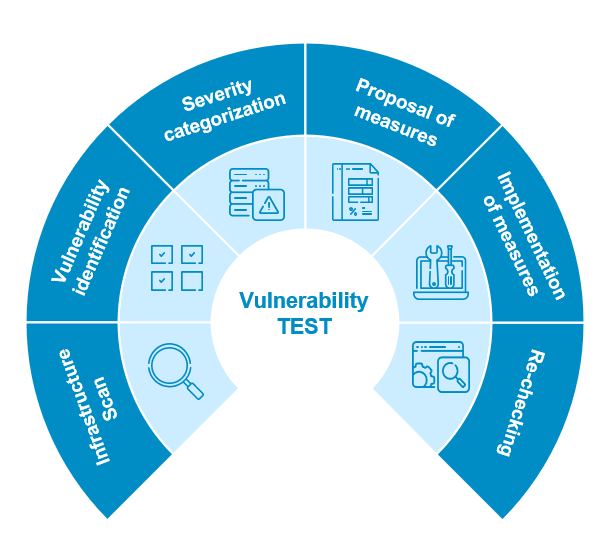
Penetration testing is a process that simulates attacks on a system, application or network in order to identify vulnerabilities.
Objectives of penetration testing
- Identify and assess vulnerabilities.
- Test the effectiveness of security measures.
- Provide recommendations for improvement.
Stages of penetration testing
- Planning: Define the objectives, scope and methodology of the testing.
- Scanning and identification: Look for vulnerabilities.
- Exploitation: Simulate attacks on vulnerabilities that are found.
- Evaluation and report: Evaluate the results and produce a report with recommendations.
Benefits of penetration testing
- Proactive approach: Penetration testing allows organisations to identify vulnerabilities before they become targets of attacks.
- Realistic scenarios: The testing simulates real-life attacks, helping organisations understand their weaknesses better.
- Recommendations for improvement: On the basis of the results of the testing, organisations receive recommendations on how to improve their cyber security.
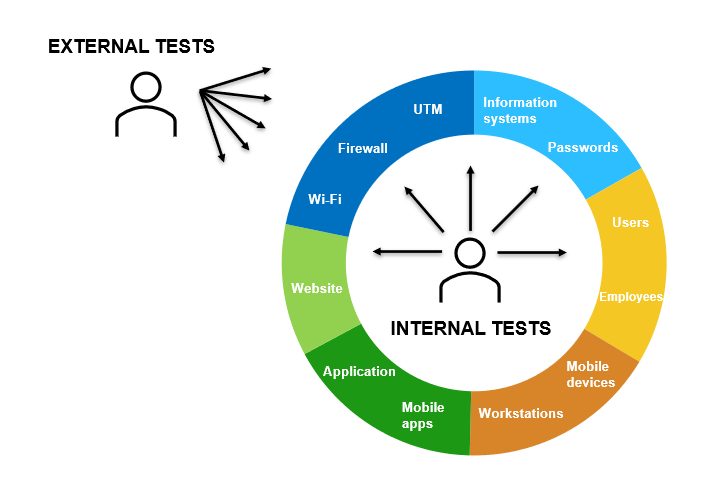
The NIS2 Directive and Cyber Security
- The Network and Information Systems Directive (NIS2) is European legislation that sets out cyber security requirements for digital service providers and critical infrastructure operators.
- Penetration testing is one of the key measures that organisations must implement to comply with the NIS2 Directive.
- Regular penetration testing helps to identify and eliminate vulnerabilities, minimise risks and protect a company’s critical infrastructure.
What does the NIS2 Directive say about vulnerabilities?
- Vulnerability identification: Organisations should audit their systems and applications for vulnerabilities regularly. This includes scanning software, network devices and web applications for potential vulnerabilities.
- Severity of vulnerabilities: It is important to classify vulnerabilities according to their severity. Some may be critical and require immediate intervention, while others may be less serious.
- Fixes and updates: Organisations should update their systems and applications regularly to remove known vulnerabilities. This includes installing security patches and fixes.
- Staff training: Educating employees about cyber security and vulnerabilities is key. Employees should be able to identify potential threats and act in accordance with security procedures.
Vulnerability and penetration testing are key elements for ensuring cyber security. Organisations should regularly conduct penetration testing, update their systems and train their staff. Compliance with the NIS2 Directive is not only an obligation, but also the basis for protecting digital infrastructure and sensitive data.
At RSM CZ, we have a team of experts who can help you with this issue. We can carry out tests, provide recommendations and take specific steps to correct any shortcomings. Do you need help or advice? Please do not hesitate to contact us.
